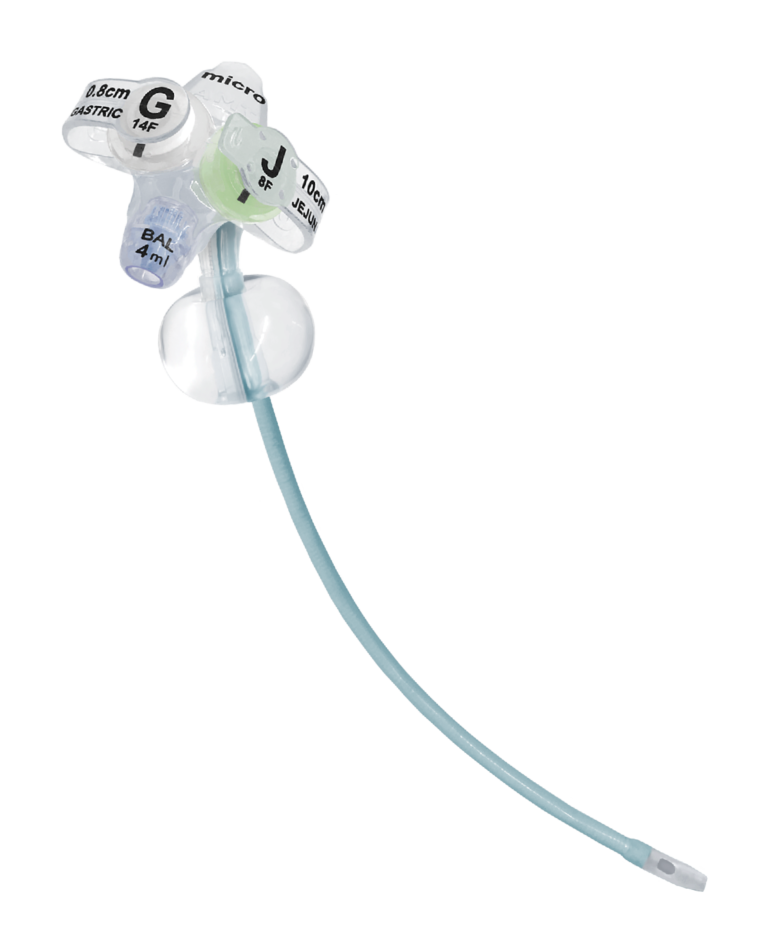
AMT’s Pediatric G-J Enteral Feeding Tube
A gastric-jejunal feeding device is inserted through the abdominal wall and into the stomach. Unlike a g-tube, which ends in the stomach, a gastric-jejunal feeding device travels into the stomach, through the pylorus, and ends in the small intestine.
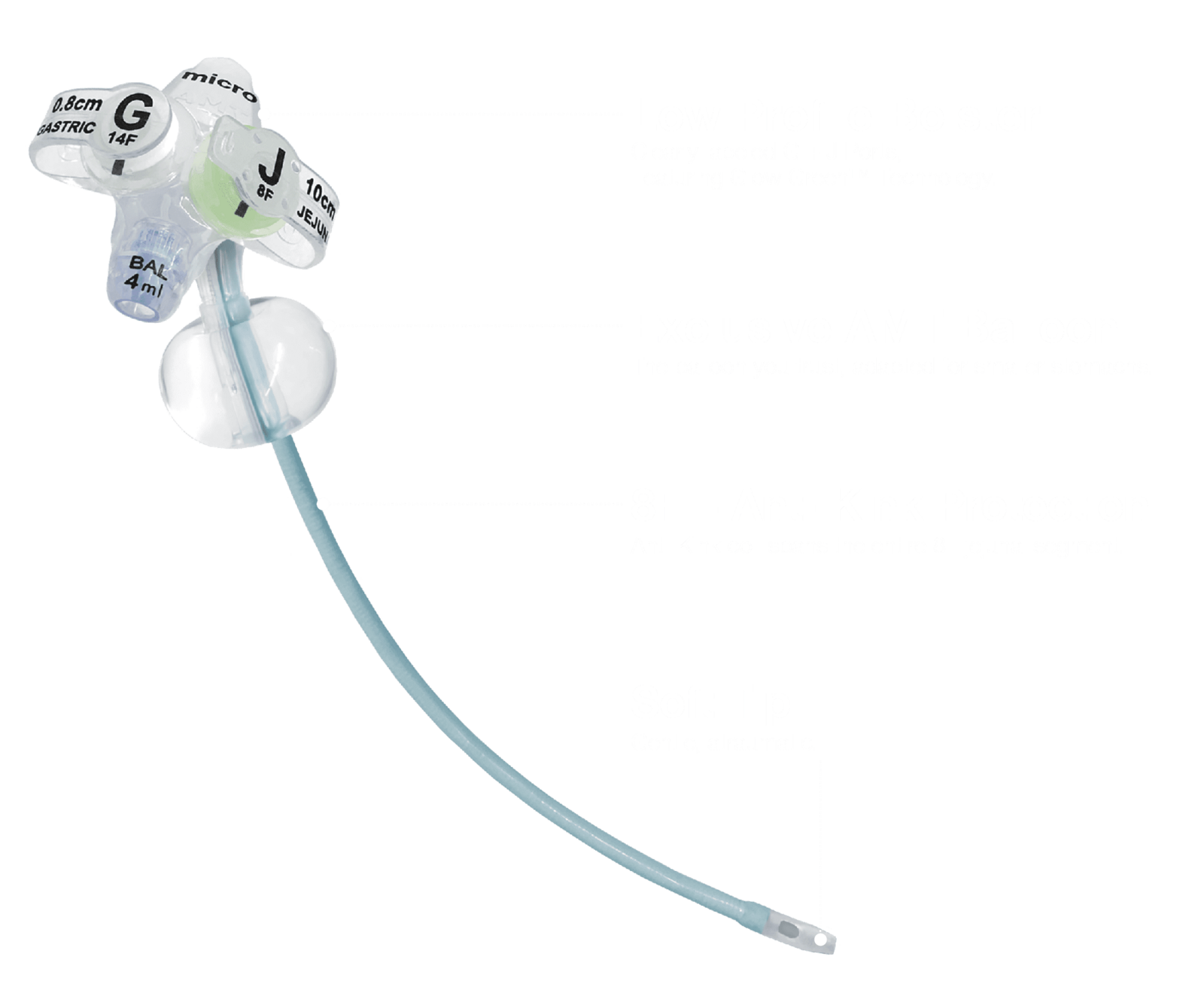
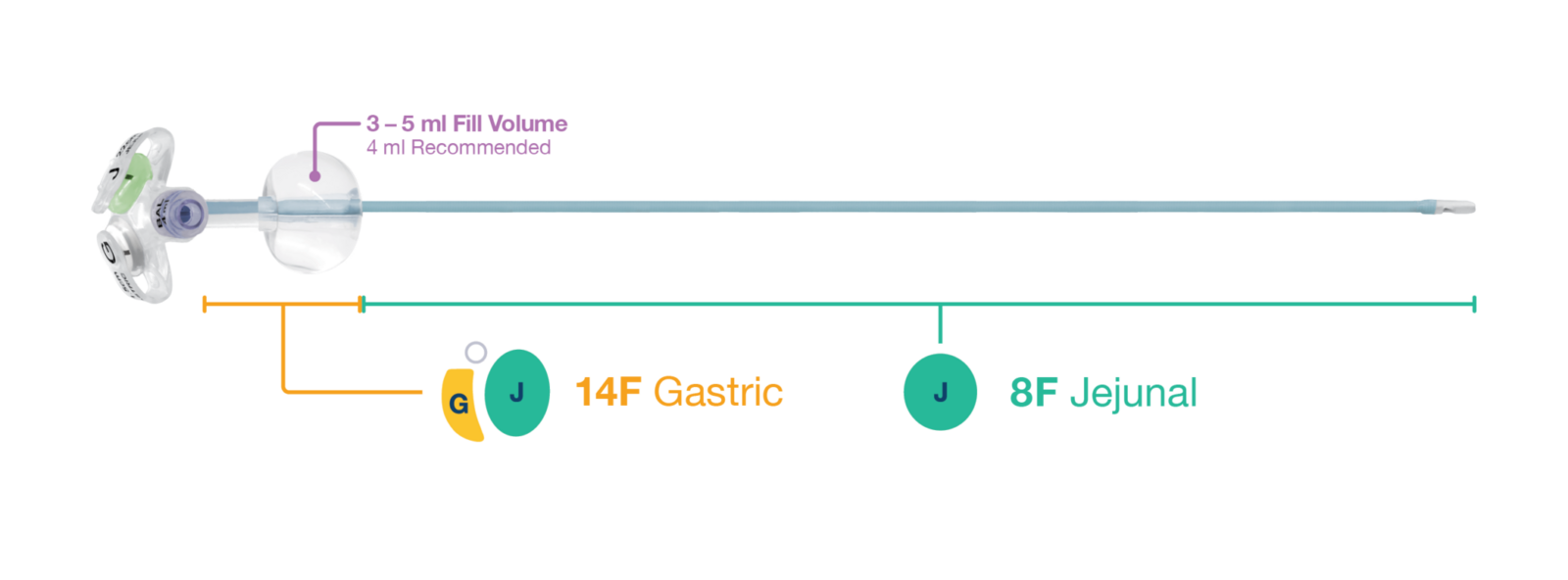
The micro G-JET® was designed to meet the enteral nutrition needs of pediatric patients. The micro G-JET® transitions from a 14F gastric segment to an 8F jejunal segment. The 8F jejunal tubing is well-suited for the narrow lumen of the small intestine in pediatric patients and was designed to reduce digestive problems associated with sustained pyloric opening, such as reflux and potential aspiration of bile or chyme.
The AMT micro G-JET® is the ONLY low profile gastric-jejunal feeding device with an 8F jejunal segment.
Click here to download the micro G-JET® brochure.
“I’m happy that AMT invested in manufacturing a GJ feeding tube that is more suitable for our pediatric patients. As a pediatric interventional radiologist, I will no longer have to use larger adult-size tubes or resort to using our own “homemade GJ” devices for these smaller patients. The micro G-JET® feeding tube was truly designed for and will benefit infants as small as six kg who depend on long term enteral nutrition,” said Karun Sharma, MD, Director of Interventional Radiology, Children’s National. “It’s really great to see a company invest in the health and wellbeing of pediatric patients.”

Enhanced Features: Designed for Pediatric Patients*
Low Profile Bolster
With clearly labeled G + J ports
Exclusive AMT Balloon
The balloon you trust, adapted for smaller stomachs
Anti-Kink Protection
Spans the entire 8F jejunal segment
“I am so impressed with the micro G-JET®,” said Daniel Saltzman, MD, PhD, Surgeon-in-Chief, University of Minnesota. “It is a complete game changer for our patients.”
micro G-JET® Button Sizes –
14F Gastric x 8F Jejunal
Part Numbers & Ordering Information
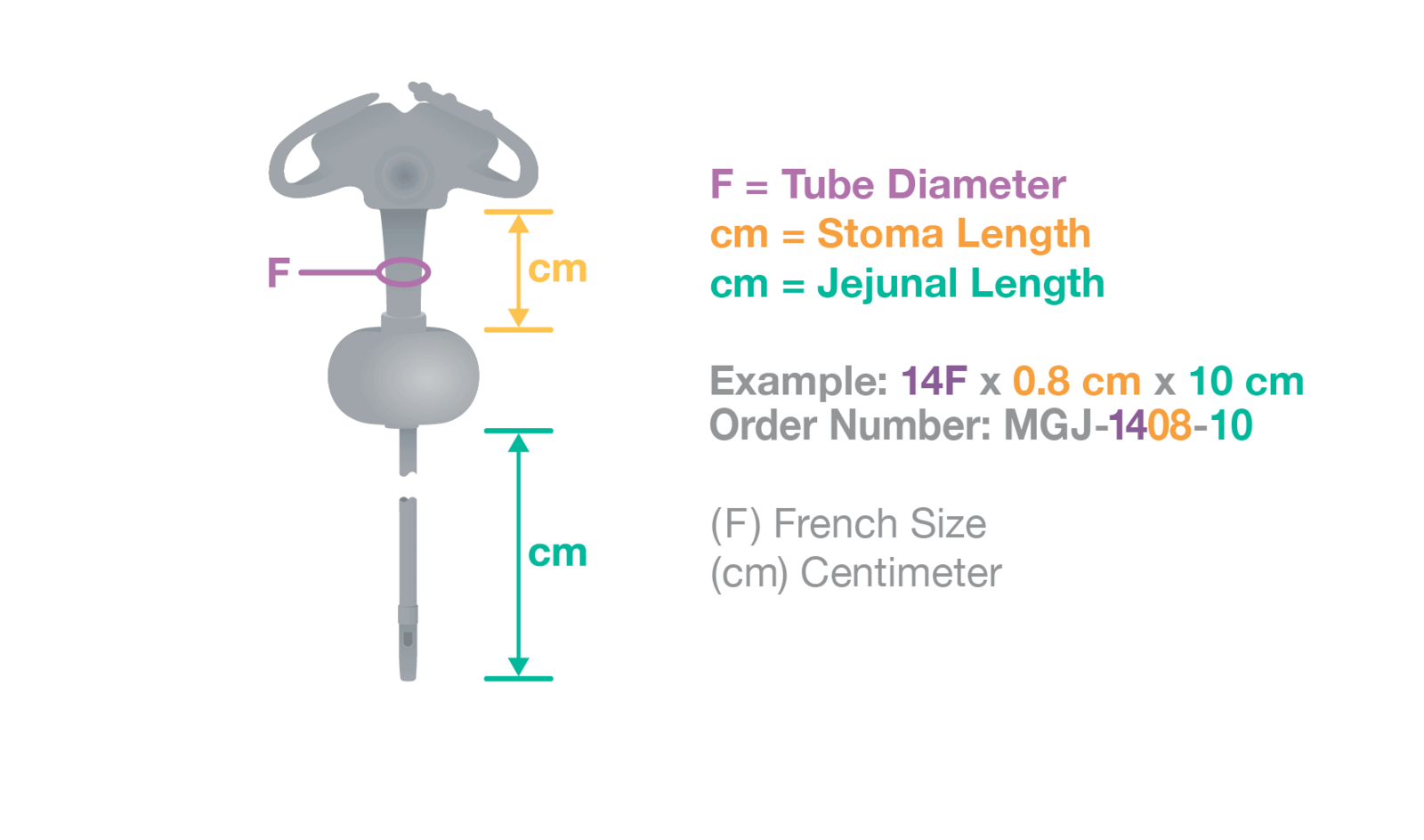
The micro G-JET® is available in 14F with stoma lengths ranging from 0.8 cm to 2.5 cm with jejunal lengths ranging from 10 cm to 30 cm.
Healthcare professionals can order with established NET 30 terms or prepayment/credit card.
NOTE: The micro G-JET® may be placed percutaneously under fluoroscopic or endoscopic guidance or as a replacement to an existing device using an established stoma tract.
Placement/removal is to be performed by a qualified clinician.
NOTE: the micro G-JET® should never be cut to custom lengths.
The micro G-JET® is cleared for initial placement and is MR Conditional.
micro G-JET® Gastric + Jejunal Sets
AMT Accessories
AMT is at the forefront of enteral nutrition innovations. We do our best to meet the individual needs of all of our customers with every innovation. We try to be there for every user’s needs, whether it’s feeding before bedtime, placing a new button, or simply taking medicine. AMT accessories provide tools to help you use AMT devices and enhance your experience.
Check out all AMT Accessories HERE!
Frequently Asked Questions
AMT has provided this information as an educational resource tool. This is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care.
Your FIRST source of information should be your healthcare provider.
How does the micro G-JET® device work?
- The micro G-JET® is a low profile gastric-jejunal enteral feeding tube, also known as a GJ-Tube.
- A GJ-Tube, like the micro G-JET®, is recommended for people who cannot eat by mouth and have a stomach that does not work properly. These patients need to use the small intestine to get nutrition to the body – the GJ-Tube allows them to do that!
- The GJ-Tube is placed through the belly, or abdominal wall. The full length of the GJ-Tube extends from the abdominal wall, through the stomach, and into a part of the small intestine called the jejunum.
- The GJ-Tube has two ports: the gastric port (g-port) goes to the stomach and is most commonly used for delivering medication, draining excess fluids, or venting air; the jejunal port (j-port) goes to a section of the small intestine called the jejunum and is used to deliver nutrition.
- You can think of the GJ-Tube as being two tubes in one. The first tube ends in the stomach, and the second tube ends in the small intestine (specifically, the jejunum).
- The phrase “low profile” means that the external portion of the device, often called the bolster, is very flat or flush against the skin. Low profile GJ-Tubes, like the micro G-JET®, are sometimes called a button.
What’s included in the micro G-JET® Button device kit?
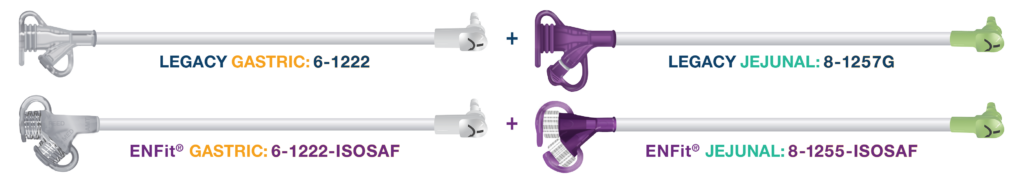
- micro G-JET® Legacy Kit Contents
- 6-1222 Gastric Extension Set (12” right angle connector with y-port adapter)
- 8-1257G Jejunal Feed Set (12” right angle connector with y-port adapter)
- 5 ml slip tip syringe
- 35 ml syringe
- Winged Luer adapter attached to 10 ml syringe
- Guidewire adapter (for physician use during placement)
- micro G-JET® ENFit® Kit Contents
- 6-1222-ISOSAF Gastric Extension Set (12” right angle connector with ENFit® y-port adapter)
- 8-1255-ISOSAF Jejunal Feed Set (12” right angle connector with ENFit® y-port adapter)
- 5 ml slip tip syringe
- 35 ml ENFit® syringe
- Winged Luer adapter attached to 10 ml syringe
- Guidewire adapter (for physician use during placement)
What are the flushing recommendations for the micro G-JET®?
AMT recommends flushing the micro G-JET® every 4 hours with 1-2 ml of water (or amount prescribed by the healthcare team) during continuous feeding to avoid clogging and to maintain tube patency. DO NOT USE FORCE.
- Use a 30 to 60 ml syringe. Do not use smaller size syringes as this can increase pressure on the tube and potentially damage smaller tubes.
- Use room temperature tap water for tube flushing. Sterile water may be appropriate where the quality of municipal water supplies is of concern.
- The amount of water will depend on the patient’s needs, clinical condition, and type of tube – the average volume ranges from 10 to 50 ml for adults, and 3 to 10 ml for infants.
- Hydration status also influences the volume used for flushing feeding tubes. In many cases, increasing the flushing volume can avoid the need for supplemental intravenous fluid. However, individuals with renal failure and other fluid restrictions should receive the minimum flushing volume necessary to maintain patency.
- Flush the feeding tube before and after medication administration and between medications. This will prevent the medication from interacting with formula, potentially causing the tube to clog. Use liquid medication when possible and consult the pharmacist to determine if it is safe to crush solid medication and mix it with water. If safe, medication should be crushed as fine as possible (into powder form) and dissolved into water before administering through the device. Never crush enteric-coated medication or mix medication with formula. Avoid using acidic irrigants such as cranberry juice and cola beverages to flush feeding tubes, as the acidic quality combined with formula proteins may actually contribute to tube clogging.
- Do not use excessive force to flush the tube. Excessive force can damage the tube and can cause injury to the gastrointestinal tract.
- Document the time and amount of water used in the patient’s record. This will enable all caregivers to monitor the patient’s needs more accurately.
There is leaking around the micro G-JET®; what should I do?
There are many reasons why the micro G-JET® might leak. Some of the most common reasons include:
- Low Water Level in the Balloon. Make sure the balloon is filled with the correct amount of water (resistance should be felt when gently pulling on the tube.) NOTE: The recommended amount of water for the balloon is printed on top of the balloon fill valve. If you have questions, contact your healthcare provider.
- Incorrectly Sized Device. If the micro G-JET® feels too tight or too loose, make sure that the French size and stoma length match what is prescribed by your healthcare provider. If the wrong device is in place, contact your provider.
- It is important to have your stoma site re-measured on a regular basis, especially if you are still growing or have lost/gained weight recently. Changes to your body may impact the size of the device you need. If you are not experiencing changes to your body, the stoma site should still be measured every 6-12 months for optimal device performance.
- Newly Placed micro G-JET®. For new placements, it may take time for the stoma tract to naturally heal and firm up around the tube and the balloon. If leakage continues, contact your healthcare provider.
The feed set disconnected from the micro G-JET®; what should I do?
- Immediately stop the feeding pump, clamp off all extension tubing, and thoroughly clean the micro G-JET® feed port and the feed set connector with soap and water. CLEAN THE INSIDE OF THE FEED SET AND THE DEVICE FEEDING PORT WITH A CLEAN COTTON SWAB AND SOAP AND WATER. Dry the connector and then reconnect the feed set. You may want to add a small amount of extra formula to make up for what was lost and continue the feeding.
The micro G-JET® dislodged (came out); what should I do?
- Although the micro G-JET® is designed to reduce the risk of a pull out, the device may become accidentally dislodged (pulled out) from the stoma.
- If the micro G-JET® is partially dislodged (the device is still inside the stoma):
- Stabilize the micro G-JET® in place and call your physician.
- DO NOT REMOVE the micro G-JET® until a replacement is available in order to prevent the stoma from closing.
- If the micro G-JET® is NOT in place and has come completely out of the stoma:
- Call your physician and schedule an appointment immediately.
- ALWAYS have a stoma plug or a spare G-Tube, like the AMT MiniONE® Balloon Button, available in case the micro G-JET® becomes dislodged. The backup device should match the French (F) size and gastric (stoma) length of your current micro G-JET® device. If your micro G-JET® falls out, placing a spare stoma plug/G-Tube into the stoma will help prevent the stoma from closing. Follow the Directions for Use and your healthcare provider training to properly place the G-Tube in the stoma.
- Inserting a device that is too long or too short into your stoma site is not recommended.
- THE STOMA WILL CLOSE VERY QUICKLY IF THE SPARE G-TUBE IS NOT PLACED IN RIGHT AWAY, AS EARLY AS TWENTY-FOUR (24) HOURS FROM WHEN IT FALLS OUT.
I think the micro G-JET® has a clog; what should I do?
- WARNING: DO NOT USE EXCESSIVE FORCE OR PRESSURE WHEN ADMINISTERING FEED OR MEDICATION OR TO ATTEMPT TO CLEAR A CLOG IN THE TUBING. THIS CAN CAUSE THE TUBING TO RUPTURE OR LEAD TO DAMAGE OF THE TUBING SUPPORT STRUCTURE. IF CLOG CANNOT BE CLEARED OR TUBING IS CLOGGING ON A FREQUENT BASIS, THIS MAY INDICATE THAT THE DEVICE NEEDS TO BE REPLACED.
- Make sure that the feeding tube is not kinked or clamped off.
- Fill a catheter tip syringe with warm water (always use a 30 ml – 60 ml syringe). Insert the tip of the syringe into the purple adapter of the feed or extension set. If you suspect the clog is in the jejunal section of the micro G-JET®, connect the syringe to a feed set (Glow Green™ connector); if you suspect the clog is in the gastric section of the micro G-JET®, connect the syringe to an extension set (white connector). Gently push warm water through the feed/extension set until all of the air is removed from the tubing. Close the pinch clamp on the feed/extension set and then attach the connector to the appropriate port of the micro G-JET® device.
- CAUTION: Do not use a syringe less than 30 ml, as smaller syringes (such as 10 ml) can create high pressure very quickly and may negatively impact the device.
- Release the pinch clamp and gently push and pull the syringe plunger to free the clog. It may take several cycles of pushing/pulling the plunger to clear the clog.
- If you are unable to remove the clog, repeat steps #1-3 with a new solution of warm water. Pushing and pulling on the syringe plunger will likely break up the clog.
- If the clog cannot be removed, contact your healthcare professional, as the micro G-JET® may need to be replaced.
- Do not use cranberry juice, cola drinks, meat tenderizer, or any other medicines, as they can actually cause clogs or make things worse in some patients.
- Do NOT place any objects except the appropriate extension set or feed set into the micro G-JET® ports. Inserting foreign objects into the micro G-JET® ports could damage the micro G-JET® and negatively impact device performance.
What is the MR status of the micro G-JET®?
- The micro G-JET® is considered MR Conditional, which means that the tube has metal present within it – but has undergone testing to show that, under specific conditions, it is safe for a patient with a micro G-JET® to have an MRI. The specific MRI conditions are listed on the device safety card included in the product packaging.
- NOTE: AN MR (MAGNETIC RESONANCE) ENVIRONMENT SAFETY CARD HAS BEEN PLACED IN THE DEVICE KIT. PLEASE KEEP THE CARD WITH YOU FOR YOUR RECORDS. THIS CARD CAN BE GIVEN TO YOUR RADIOLOGIST IF AN MRI IS NEEDED.
How do I care for my stoma site/device?
- Cleaning: The stoma site should be kept clean and dry at all times. It is important to clean the stoma site every day. Use a cotton swab or terry cloth to clean the skin around the micro G-JET® with mild soap and water, or follow what your provider has advised you to do.
- DO NOT TURN OR TWIST the micro G-JET® AROUND IN CIRCLES. Gastric-Jejunal tubes must NOT be turned because they may kink. If the tube becomes kinked, call your provider.
- Bath Time: Patients fitted with a micro G-JET® are allowed to bathe and swim. Be sure to close the safety plugs before submerging the device in water. Bath time is a good opportunity for routine cleaning of the micro G-JET® and the stoma site.
- After Cleaning: Always let the stoma site air dry after cleaning.
- Always check the stoma site for redness, pain/soreness, swelling, or any drainage. If you notice any of these signs or symptoms, contact your healthcare provider.
*The micro G-JET® is cleared for patients > 6kg.
ENFit® is a registered trademark of GEDSA, Inc. or its affiliates.
 Order Info
Order Info